An Indian firm has partnered with Israeli Elbit Systems to locally manufacture the Precise and Universal Launching System (PULS) multiple rocket launcher (MRL) locally.
Nibe Defence and Aerospace Limited, a private defense manufacturing company, has inked a deal to build the Israeli company’s Precise and Universal Launching System (PULS) multiple rocket launcher (MRL) in India.
In a July 28 filing to the National Stock Exchange (NSE), Nibe stated that the MRL will be developed locally and delivered to the Indian military, should the service approve its acquisition.
The agreement includes transfer of technology (ToT) to the Indian manufacturer, which will give a big boost to the ‘Make in India’ initiative, enhance domestic manufacturing capabilities, and position India as a global supplier of artillery systems.
If acquired by the Indian Army, PULS would be the first universal rocket launcher to be operated by the country.
The Universal Rocket Launcher, to be named SURYA, is a highly advanced system capable of engaging targets with precision over a range of up to 300 kilometres.
“The Universal Rocket Launcher is set to revolutionise modern warfare with its remarkable capabilities and performance, positioning NIBE Limited as a key player in the global defense sector,” NIBE earlier said in a press release.
India currently operates the Pinaka MBRLS (Multiple Barrel Rocket Launch System), which is a free-flight artillery rocket area bombardment system. A single Pinaka system fires 12 rockets from a multi-barrel launcher in 44 seconds, while a battery can fire 72 rockets.
The 214mm bore Pinaka Mk-1 rocket has a payload of 100 kilograms and can be fitted with various warheads, such as anti-tank mines and blast-cum-pre-fragmented high explosives. The Pinaka Mk 1 has a range of 37.5 kilometers.
Meanwhile, Pinaka Mk 2 214 mm rockets feature a 250-kilogram warhead and have an enhanced range of over 60 kilometres, and the Pinaka Extended Range (ER) variant has a range of 60-90 kilometers.
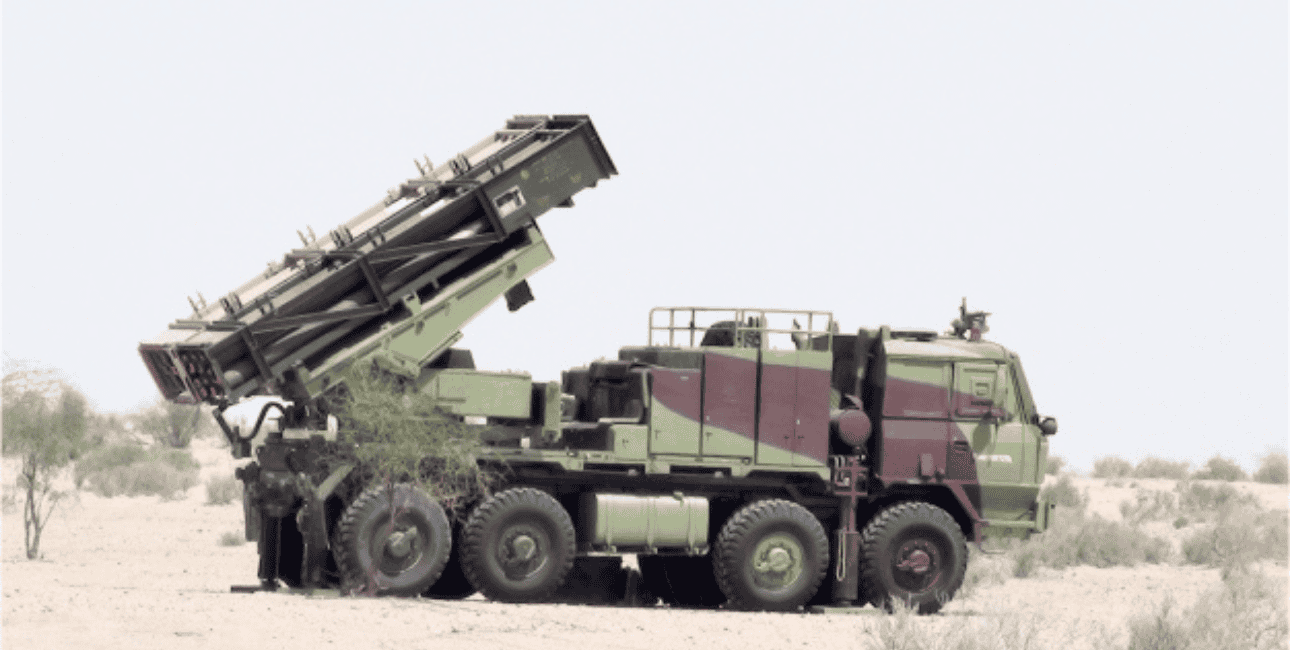

Notably, India has been pushing Pinaka MBLRS, which is often compared to the combat-hardened HIMARS (High Mobility Artillery Rocket Systems), in the export market.
Armenia became the first buyer of this indigenously developed system in November 2024, and France had earlier explored the possibility of acquiring the system.
The Pinaka rocket system, named after Lord Shiva’s divine bow, gained its first combat experience in the 1999 Kargil conflict against Pakistan. The battles in the frigid Himalayan mountain ranges saw Pinaka neutralize Pakistani positions on mountain tops.
The Defence Research and Development Organization has enhanced the range of the system, with Pinaka Mk2, which has a range of 60 kilometres.
Despite these cutting-edge capabilities and its successful combat record, Pinaka does not have the universal launch capability or the range that matches the PULS.
The production of the vaunted PULS locally will, thus, enhance the capabilities of the Indian armor and enable it to leverage the production to become a world-class artillery exporter at a time when the world has accepted that “artillery is the king.”
Is The PULS Superior?
Developed by Elbit Systems of Israel, the PULS (Precise & Universal Launching System) is a highly modular, cost-effective, and advanced multi-rocket launcher (MRL) designed to fire a diverse range of rockets and missiles from a single platform.
Designed for maximum flexibility, PULS supports a range of rocket calibers, enabling operators to choose different munitions based on mission requirements. For instance, it can launch 122 mm rockets with a range of 40 kilometres; 160 mm rockets with a range of 45 kilometres; 306 mm rockets with a range of 150 kilometres; and Heavy rockets and missiles like the EXTRA and Predator Hawk, capable of 300 kilometres of range.
It, thus, embodies the concept of a universal rocket launcher.
PULS has a platform-neutral design with a modular architecture. It can be integrated on a variety of wheeled or tracked chassis, including 4×4, 6×6, and 8×8 configurations.
It is designed to be integrated with national fire-control systems, allowing user countries to choose and use their own munitions. Moreover, the system can operate in a variety of environments, including rocky mountainous regions, metropolitan areas, and vast deserts.
Unlike other comparable MLRS, the PULS has a low cost of maintenance due to its commonalities across platforms that reduce the cost of training and spare parts.
Notably, the PULS System can be integrated into existing command-and-control networks or operate autonomously, receiving targeting data directly from UAVs, radar, or forward observers. It is, thus, tailored for modern warfare, offering precision, rapid deployment, and adaptability across various platforms and combat scenarios.
With automated reloading for prolonged operations, it can complete a shooting mission in less than a minute. It uses GPS-based navigation for high accuracy, with a Circular Error Probable (CEP) of 10 meters for guided munitions.
It integrates advanced C4I (Command, Control, Communications, Computers, and Intelligence) systems and supports network-centric warfare. Additionally, it incorporates advanced countermeasures and loitering munitions for real-time battlefield assessment.
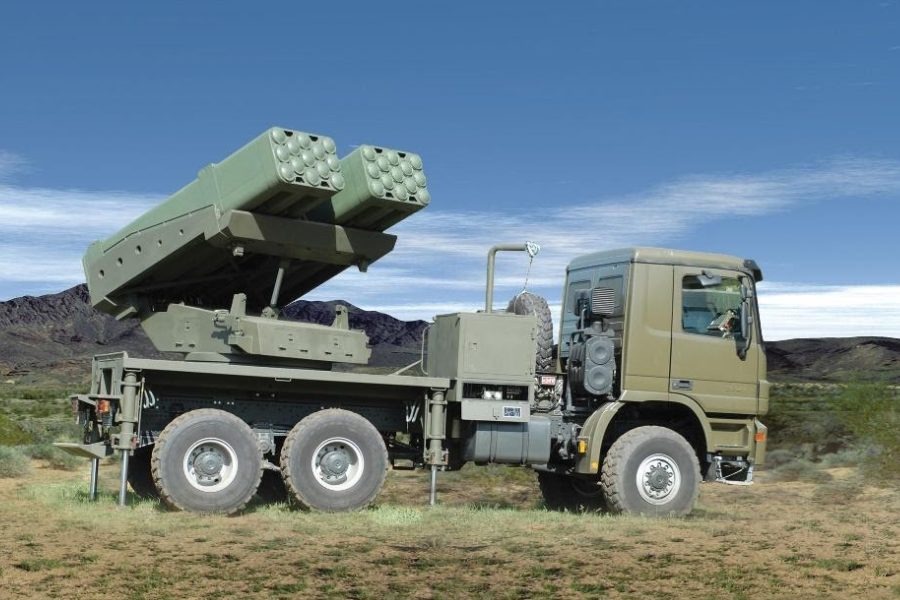

The PULS system, produced by Elbit Systems, has proven to be a viable alternative to HIMARS. For example, countries like the Netherlands and Germany selected PULS because it offered a quicker delivery timeline than HIMARS. Moreover, this Israeli system offers similar capabilities at a more affordable price and with additional features.
The PULS system is also touted as adaptable to future missiles, with both KNDS and Elbit promoting its potential to evolve and integrate with various missile providers.
According to the Defense expert Sébastien Roblin, “Israel’s PULS units can also launch the subsonic Delilah cruise missile, flying much lower and slower, out to 155 miles and with even greater accuracy. The Delilah, however, doesn’t seem to be up for export.”
While India’s Pinaka MBRL is a capable system, the adoption of PULS will address the existing gaps in capability. While India has planned more advanced Pinaka variants with an extended range of 120 and 300 kilometers, respectively, a locally built variant of PULS will offer instant access to a proven system with ranges up to 300 kilometers.
The Indian military will benefit from PULS’s ability to fire long-range missiles and loitering munitions. Thus, enhancing the country’s ability to strike deep targets, as it faces threats across diverse terrains from adversaries like China and Pakistan.
India currently operates Russian-origin systems like the BM-21 Grad and Smerch MBRLs, which are less advanced and rely on foreign supply chains. PULS, manufactured as SURYA, will provide a domestically produced, cutting-edge alternative.
More importantly, though, the PULS/SURYA will complement Pinaka by offering longer-range missiles and loitering munitions, creating a layered artillery capability that will significantly enhance the Indian Army’s firepower capability